Is Jaggery Good for Diabetics? An In-Depth Look at Its Glycemic Index and Health Implications
Jaggery, a natural sweetener made from sugarcane juice or palm sap, is often praised for its nutritional benefits and rich flavor. Unlike refined sugar, which undergoes extensive processing and loses many of its nutrients, jaggery retains its natural vitamins and minerals. But when it comes to diabetes management, many wonder: Is jaggery good for diabetics, or does it pose similar risks as other sweeteners? This blog explores the myths and realities surrounding jaggery’s health benefits for diabetics, focusing on its glycemic index (GI) and overall impact on blood sugar levels.
What Makes Jaggery Different from Sugar?
At its core, jaggery is an unrefined form of sugar. The process of making jaggery involves boiling down sugarcane juice or palm sap until it thickens into a dense, golden-brown paste, which is then molded into blocks. Unlike refined sugar, which is processed to remove molasses and other nutrients, jaggery retains essential minerals such as iron, magnesium, potassium, and calcium. This has led many to believe that jaggery is a healthier alternative. However, despite its nutrient content, the question remains: Is jaggery good for diabetics?
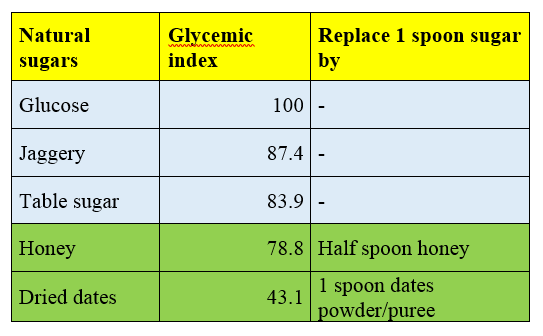
Glycemic Index of Jaggery: What Does It Mean for Diabetics?
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a measure that ranks foods on a scale from 0 to 100 based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels after eating. Foods with a high GI are rapidly digested and absorbed, leading to a swift spike in blood sugar levels. Jaggery has a GI of around 84-88, which is considered high. This is comparable to refined sugar, meaning that jaggery can cause a significant increase in blood sugar levels. For diabetics, who need to manage blood sugar levels carefully, this raises a red flag.
So, is jaggery good for diabetics? Based on its high glycemic index, the answer leans towards caution. While jaggery might be less processed than refined sugar, its impact on blood sugar can be just as potent.
Nutritional Benefits: Myth or Reality?
While jaggery does offer some nutritional benefits over refined sugar, such as retaining more vitamins and minerals, these benefits are often outweighed by its high sugar content. For example, jaggery is a good source of iron and can help prevent anemia in some cases. However, the amount of jaggery needed to make a significant impact on iron levels would also contribute a substantial amount of sugar to the diet, which is not advisable for diabetics.
Moreover, the belief that jaggery is inherently healthier than sugar can lead to overconsumption. It’s important to remember that, despite its nutrients, jaggery is still a sweetener with a high caloric content. For diabetics, consuming jaggery in large amounts can lead to blood sugar spikes and other health issues.
Moderation is Key
For diabetics, moderation is key when it comes to including jaggery in their diet. While small amounts of jaggery can be consumed occasionally, it should not be considered a staple or a substitute for more diabetic-friendly sweeteners. Pairing jaggery with foods that have a low GI can help mitigate its impact on blood sugar levels, but careful monitoring and portion control are essential.
If you are diabetic and considering adding jaggery to your diet, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian. They can provide personalized advice based on your health status and nutritional needs.
The Bottom Line: Is Jaggery Good for Diabetics?
So, is jaggery good for diabetics? While jaggery does have some nutritional advantages over refined sugar, it is not necessarily a safe or ideal choice for diabetics due to its high glycemic index and sugar content. For those managing diabetes, it is essential to focus on a balanced diet rich in low-GI foods and to use any sweeteners, including jaggery, sparingly.
Ultimately, the key to managing diabetes effectively is to maintain a balanced diet, keep a close eye on blood sugar levels, and make informed choices about all foods consumed, including natural sweeteners like jaggery. By doing so, you can enjoy the occasional sweetness of jaggery without compromising your health.
For more information on how jaggery is made and its health implications, visit our detailed guide here: How Jaggery is Made: From Sugarcane to Your Table.
